@dr.pongbonetalk เช็กด่วน สีอุจจาระแบบนี้ อาจเป็นมะเร็ง!!#หมอกระดูก #ขับถ่ายยาก #ขับถ่ายดี #อุจจาระออกเลือดเกิดจากอะไร #สีอุจจาระบอกโรค #หมอ #แพทย์ #หมอโป้ง #คุยเฟื่องเรื่องกระดูก #มะเร็ง #มะเร็งระยะสุดท้าย #มะเร็งตัวร้าย #ผู้ป่วยมะเร็ง #เทรนด์วันนี้ @หมอโป้ง คุยเฟื่องเรื่องกระดูก @หมอโป้ง คุยเฟื่องเรื่องกระดูก @หมอโป้ง คุยเฟื่องเรื่องกระดูก ♬ Panek Di Awak Kayo Di Urang - DJ Lunox
Our stool is one of the best indicators of our health! If you notice any changes in the color, smell, or appearance of yours without a known cause, do not ignore it. These changes could be warning signs of serious underlying conditions, such as colorectal cancer, stomach diseases, or even gastrointestinal bleeding. Regularly checking your poop is crucial to detect abnormalities early before the condition worsens.
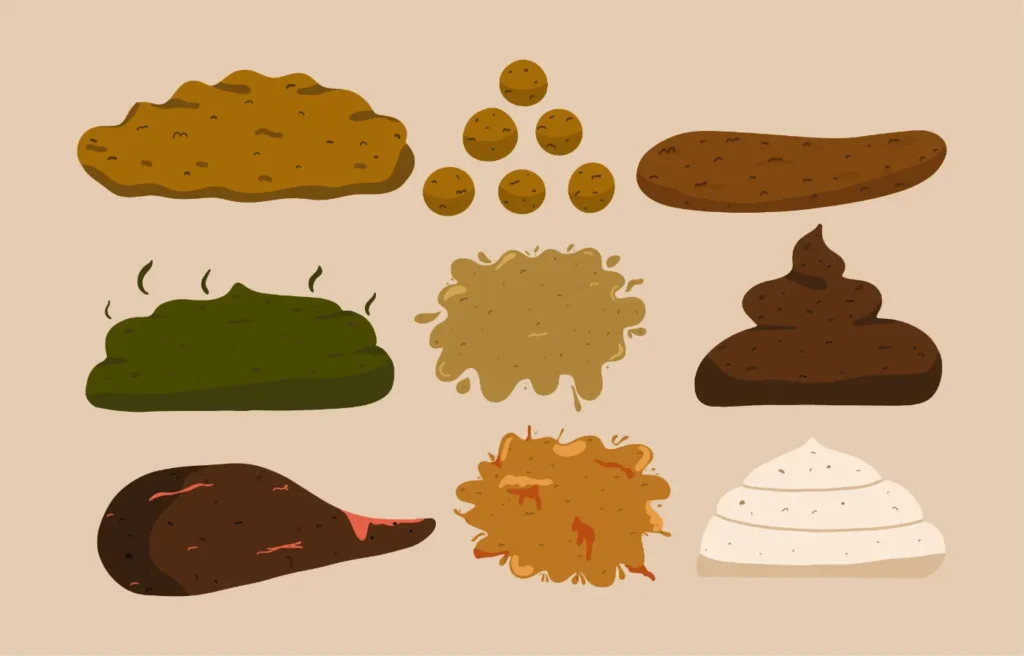

1. The Importance of Stool Color
The color of your stool is a significant indicator of your overall health. Changes in poop color can reveal hidden health issues within the digestive and excretory systems. Observing and understanding the poop color meaning is essential as it can help you recognize health problems early and seek timely treatment.
Stool Color and Cancer: The Relationship Between Stool Color and Cancer
The color of your poop can indicate significant health issues, particularly colorectal cancer, which is common among Thais. Symptoms to watch for include stool with blood or dark red stool, which may signal bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, in colorectal cancer, other symptoms to be aware of include irregular bowel movements such as alternating constipation and diarrhea, narrower stools, or mucus mixed with blood. Screening for colorectal cancer is the best method to prevent and treat this disease in its early stages.
Stool Color and the Digestive System: Indicators of Health Problems
The color of your poop can indicate various health issues within the digestive system. Green stool may result from consuming large amounts of green leafy vegetables or certain medications, such as those containing iron. Additionally, green stool can be a sign of diarrhea or an infection in the digestive system. Black stool may indicate bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, or small intestine. Yellow stool that is greasy and foul-smelling may signal malabsorption issues. Changes in stool color can be caused by various factors, such as consuming foods with synthetic colors, taking certain medications, or having underlying health problems. Observing the color of your stool is a good way to monitor the health of your digestive and excretory systems.
2. Stool Colors Indicating Serious Diseases
Observing the color of poop is one method to indicate the health of the digestive and excretory systems. Changes in poop color can be warning signs of serious diseases that require timely diagnosis and treatment.
Red Stool: A Sign of Colorectal Cancer
Red stool is one of the most concerning signs as it may indicate bleeding in the lower digestive tract, such as the colon or rectum, which could be caused by hemorrhoids or colorectal cancer. Blood in the poop can result from hard poop scraping against abnormal growths or cancerous lesions in the colon, causing bleeding.
Other symptoms that may accompany red stool include alternating constipation and diarrhea, smaller poop size, a feeling of incomplete evacuation, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, as early detection of colorectal cancer increases the chances of a cure.
Black Stool: A Sign of Gastric Bleeding
Black stool often signals bleeding in the upper digestive tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, or upper small intestine. Blood from these areas is digested by stomach acid, turning it black and giving the stool a tar-like appearance. Common causes of gastric bleeding include stomach ulcers, gastritis from aspirin or painkillers, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Other symptoms that may accompany black stool include burning pain in the upper abdomen when hungry or full, fatigue, dizziness, and fainting. If these symptoms are present, it is essential to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, as gastric bleeding can be a serious condition requiring urgent care.
White Stool: A Sign of Bile Duct Obstruction
White or pale stool indicates problems in the bile duct system, such as a blockage preventing bile from entering the small intestine. Bile gives poop its brown color, so the absence of bile results in white or pale stool. Common causes of bile duct obstruction include gallstones, bile duct infections, and bile duct cancer.
Other symptoms that may accompany white stool include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), severe abdominal pain, especially under the right rib cage, and fatigue. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, as bile duct obstruction can be a serious condition requiring urgent care.
Green Stool: A Sign of Other Health Issues
Green stool can result from consuming green-colored foods like leafy vegetables or certain medications. However, it can also be a sign of health issues such as diarrhea, food poisoning, Crohn’s disease, and gastrointestinal infections. Green stool may occur when food moves too quickly through the intestines, preventing bile from being fully broken down.
Other symptoms that may accompany green poop include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. If these symptoms are present, it is advisable to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, as they may indicate underlying health problems that need attention.
3. Prevention and Treatment
Checking Stool Color: Initial Examination Method
Examining the color of your stool is a preliminary method that can indicate the health of your digestive system and overall body. Normally, poop is brown due to the breakdown of bile in the intestines. However, the color of poop can change based on the type of food consumed or may signal certain health issues. This examination can be done independently. If you notice a change in poop color, stop consuming suspected foods or medications for 2-3 days to see if the poop color returns to normal.
Consulting a Doctor: When to Seek Medical Advice
If you notice abnormalities in your stool, such as persistent color changes or accompanying symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, or blood in the stool, you should see a doctor for further diagnosis. Diagnostic tests may include a Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) or a colonoscopy to determine the cause of the symptoms.
Symptoms that require immediate medical attention include:
- Blood in the poop or black stool
- Chronic or severe abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Unexplained fatigue
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Treatment and Prevention: Methods for Managing and Preventing Issues
Managing and preventing issues related to the digestive system and poop can be done in various ways, depending on the cause of the symptoms.
- Treatment:
- Diarrhea: If caused by bacterial or viral infections, drink electrolyte solutions to replace lost fluids and salts. For severe symptoms, consult a doctor for antibiotics or antiviral medications.
- Constipation: Eating high-fiber foods, drinking plenty of water, and regular exercise can help stimulate bowel movements. If symptoms persist, consult a doctor for laxatives.
- Colorectal Cancer: Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage of the disease. Early detection increases the chances of a cure.
- Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Choose to eat vegetables, fruits, and whole grains high in fiber. Reduce intake of high-fat foods, processed foods, and grilled foods.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water helps keep poop soft and easier to pass.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise stimulates the intestines and digestive system.
- Annual Health Check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help detect diseases early and increase the chances of a cure.

4. Medical Procedures and Tests
Stool Analysis
Stool Analysis
Stool analysis is a comprehensive diagnostic tool used to evaluate various conditions affecting the digestive tract. It includes macroscopic, microscopic, chemical, and microbiological examinations. Macroscopic examination involves observing the color, consistency, and odor of the poop. Microscopic examination can detect parasites, eggs, fat content, leukocytes, and red blood cells. Chemical tests can identify occult blood, and stool cultures can detect bacterial or fungal pathogens. Stool analysis provides valuable insights into gastrointestinal conditions and helps guide further diagnostic and treatment plans.
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
The FOBT detects tiny amounts of blood in the stool, which can indicate polyps or cancer in the colon. It is a simple test that can be done at home using a kit. The test involves collecting poop samples and applying them to a test card, which is then analyzed for the presence of blood. If the test is positive, further diagnostic tests, such as a colonoscopy, may be recommended to determine the source of the bleeding.
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
The FIT is similar to the FOBT but is more specific for detecting blood in the stool. It does not require dietary restrictions and can be done at home. The test involves collecting a poop sample with a brush and dabbing it onto a special card. The sample is then sent to a lab for analysis. The FIT is highly effective in detecting colorectal cancer and polyps.
Stool DNA Test
The stool DNA test, also known as the FIT-DNA test, detects cellular changes and blood in the poop that may indicate cancer or precancerous polyps. It is nearly as accurate as a colonoscopy for detecting colon cancer. The test involves collecting a stool sample at home and sending it to a lab for analysis. Brands like Colorguard offer this type of test. While it is highly effective in detecting cancer, it is less effective in finding polyps compared to a colonoscopy.
Regularly monitoring poop color can provide early indicators of serious health conditions, including colorectal cancer and gastrointestinal issues. Recognizing changes and seeking timely medical advice are crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and regular check-ups are essential preventive measures.
Read other related articles
Stool Color Changes by John P. Cunha, DO, FACOEP from emedicinehealth.com
- Stool Color Changes: What Does It Mean? by Benjamin Wedro, MD, FACEP, FAAEM, Karthik Kumar, MBBS from medicinenet.com
- What are the different types of poop? by Kelsey Trull, PA-C Written by Jayne Leonard from medicalnewstoday.com
- The Meaning of Poop Colors, Shapes, Sizes, and Consistency by Cathy Wong from verywellhealth.com
- Stool Color, Shape and Self Diagnosis by Pathipat Durongpongkasem, M.D. from samitivejhospitals.com